So you want to learn how to become a teacher in Texas? Well, you’re in the right place!
In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know about becoming a teacher in Texas so you can confidently take the next steps in your teacher certification journey.
Here at 240 Certification, we’ve helped 1000s of teachers get certified in Texas, so we know a thing or two about what it takes to become a teacher in the Lone Star State!
How to become a teacher in Texas
To become a teacher in Texas, you have two routes:
The traditional certification route and the alternative certification route.
For the Traditional Route, you’ll need to:
- Earn your bachelor’s degree
- Complete an EPP
- Pass your exams
- Submit your application
- Complete background check & fingerprinting
For the Alternative Route, you’ll need to:
- Decide what you want to teach
- Enroll in an approved ACP
- Obtain a Teaching Position (SOE)
- Apply for a Probationary Certificate
- Complete requirements for a Texas teaching certificate.
- Submit your application
This is just a quick overview of the two certification routes, so let’s go into more detail on each, starting with traditional certification!
Traditional teacher certification
The traditional certification route basically means getting your teacher certification by enrolling in the education program at the college you are attending.
If you go into college knowing that your end goal is to be a teacher after college, you would work with your advisor and the college, and they would make sure you were in the correct courses and programs to become a certified teacher after you graduate.
Here are the steps to becoming a teacher using the traditional route:
1. Get your Bachelor's degree
You must obtain a bachelor's degree from an accredited college or university to teach in Texas.
2. Complete an EPP
An EPP is an educator preparation program that meets the Texas Administrative Code (TAC) requirements.
Most programs require 150 hours of coursework, 50 observation hours, and passing your content exams.
3. Pass Required Exams
The TExES is the main testing series in Texas.
Which TExES exam(s) you'll need to take depends on which subject and grade level you want to teach.
But overall, you'll be required to take both content and PPR (Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities) exams.
The content exam is for the subject you want to teach.
For example, if you wanted to be a math teacher, you would take a math content exam, and if you wanted to be a social studies teacher, you would take a social studies content exam, and so on.
The PPR exam tests whether a candidate has the knowledge and skills needed to be an entry-level teacher in a public school in Texas.
The Science of Teaching Reading (STR) exam is also now required for the issuance of five certification fields:
- Early Childhood: EC – Grade 3
- Core Subjects: EC – Grade 6
- Core Subjects: Grades 4 – 8
- English Language Arts and Reading Grades 4 – 8
- English Language Arts and Reading/Social Studies Grades 4–8
EPPs differ in when they require candidates to take state exams throughout the program.
Once you have been successfully admitted into an EPP, you will need approval from your program to take the required exams for certification.
Teacher Tip
Most districts in Texas require teachers to have an ESL certification, so it is a good idea to also take the TExES ESL Supplemental exam.
4. Field Experience
If you go the traditional route, your college or university will determine how many observation hours you will need and the length of internship, clinical, or residency required for your degree plan.
5. Apply for Certification
After completing your EPP requirements, you must apply for certification by logging into your TEAL account.
Under your Educator Certification Account, you will find your ECOS account, where you can fill out the application and pay the fee.
The fee to apply for certification is $78.
Once you have successfully applied and paid for an application for certification, you will be ready for the next step.
6. Background Check and Fingerprinting
All candidates must pay a $49 fee to be fingerprinted for a national criminal history check before a Texas teacher certification can be issued.
Having a criminal history could prevent you from becoming a teacher in Texas.
Criminal histories are reviewed individually, and many factors are considered.
You can check your fingerprint status through your ECOS account by logging into your TEAL account.
Alternative teacher certification
Becoming a teacher in Texas through alternative certification includes some of the same steps as the traditional route: enrolling in a program, passing your exams, background check, etc.
One main difference is that if you are thinking about alternative teacher certification, you usually already have a bachelor’s degree and are looking to leverage that into a teaching career.
Alternative teacher certification is used mostly people who are looking to change careers or take the next step up from a paraprofessional or substitute teacher.
Let's walk through the steps of alternative certification.
1. Decide what you want to teach
Before becoming certified, you must decide what grade levels and subject areas you want to teach.
This will help you determine the program you want to enroll in and what certification tests you must take and pass.
2. Pick an approved ACP
Once you know what subject(s) and grade level(s) you want to teach, it’s time to pick an Alternative Certification Program (ACP).
The Texas Education Agency (TEA) made this process easier by creating a list of all the approved ACPs!
To access the list, simply visit the TEA website and navigate to the ACP page.
Once there, you can filter out other alternative certification programs by selecting the "Alternative" option.
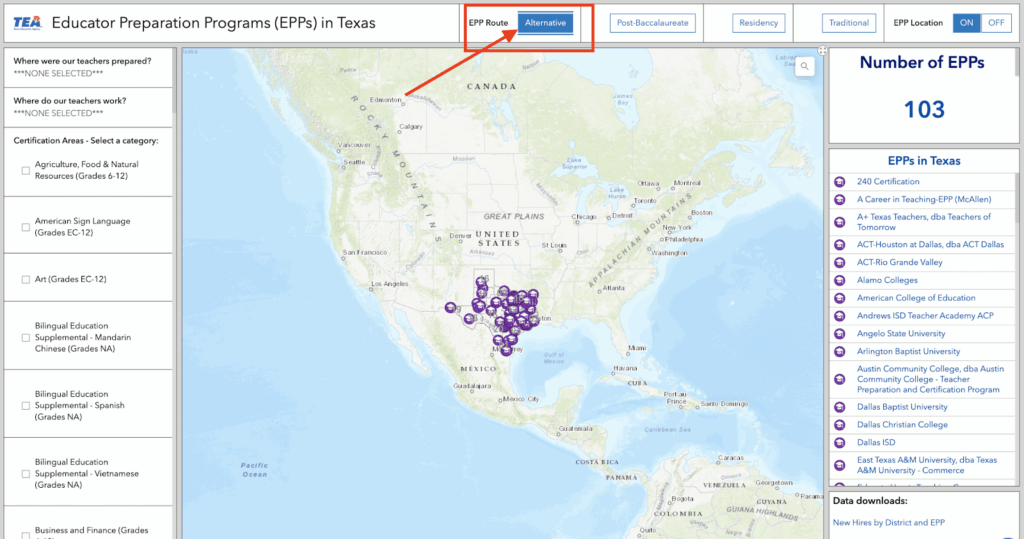
This will give you a full list of TEA-approved ACPs in Texas that meet the necessary standards and requirements.
3. Apply for ACP
To apply for an alternative certification program, you must have a bachelor's degree or be in the final semester of receiving your bachelor's degree.
Another entry requirement is having a 2.5 GPA.
If your overall GPA is less than 2.5, your last 60 hours will be calculated to see if it reaches 2.5.
You may be required to take the Pre-Admission Content Test or PACT if your GPA is lower than 2.5 or you need more coursework hours to support the certification area of your choice.
Some of these requirements are state-mandated, but individual ACPs may have additional requirements for acceptance.
*Calculate your last 60 hours here: GPA Calculator
Teacher Tip
Many programs will accept a passed Pre-Admission Content Test or PACT instead of a 2.5 GPA.
4. Start Working on your Program Requirements
Once you’ve been accepted into your program, you will start working to complete the program’s requirements.
These are some of those things we mentioned before that are very similar to the traditional route.
These requirements include passing your content tests, meeting your 50-hour observation requirement, and completing 150 hours of coursework.
5. Obtain a Teaching Position - SOE
Once you are eligible for a teaching internship or position (which is after you have completed the requirements listed in step 4) you will be provided with an eligibility statement, more commonly known as a Statement of Eligibility (SOE) for employment purposes.
This statement will allow you to be a completely hirable teacher!
Note: if you are going the intern route, you must obtain a teaching position that is the grade level and subject area of your target certification.
6. Apply for an Intern or Probationary Teaching Certificate
Once you have secured an internship, you must apply for an intern or probationary teaching certificate.
The only way to be able to apply for an intern or probationary certificate is by being enrolled in an approved educator preparation program and completing a supervised internship at a TEA-accredited school.
You must have passed one or more content exams tied to your certification area to obtain your intern certificate.
You must have passed all of your content and PPR exams to obtain a probationary certificate. Both of these certifications are valid for one year and will require you to get a criminal background check.
7. Complete all requirements for a Texas teaching certificate.
To obtain a standard certification, candidates must complete program requirements, including observations, coursework, and a successful clinical experience (clinical teaching or a full-year internship, serving as a paid teacher of record) and pass all content and pedagogy exams.
8. Apply for a standard Texas teaching certificate.
Once you have completed all your requirements, you will apply for a standard teaching certificate in Texas.
You will be required to complete the appropriate paperwork, forms, and fees.
When your certificate is approved, it will be posted to the Texas Education Agency (TEA) website, and you will receive an email notification.
Then, you will be legally certified to teach in Texas! Yay!
Which path is right for you?
Now that we’ve broken down the two certification routes, now it’s time for you to pick which route works best for you!
Traditional certification is best suited for those without a bachelor’s degree or for those who plan to pursue a graduate degree.
For individuals who already hold a bachelor’s degree and wish to transition into teaching quickly and affordably, the alternative certification path is ideal.
Here To Help You Become A Teacher In Texas!
240 Certification specializes in helping teachers become certified in Texas. We create personalized plans tailored to your specific needs, and you will have a dedicated advisor to guide you throughout the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Unfortunately, no. While you cannot be a teacher of record, you can be a substitute teacher or paraprofessional. So, while the answer is no to being a certified teacher, there are still many ways you can be a part of education! Many Texas school districts allow substitute teachers with a high-school diploma or GED to substitute teach. You need to check with individual districts to know what qualifications they require of their substitutes and paraprofessionals. Many districts in Texas have a substitute shortage and encourage those passionate about teaching to apply!
This answer might shock you! Did you know you can become a teacher in Texas in as little as 12-18 months? With a teacher alternative certification program like 240 Certification, you can apply once you are in the final semester of completing your Bachelor’s degree. Already completed a Bachelor’s degree? Great! Your journey to teacher certification in Texas can begin now with 240 Certification.
Absolutely! If you want to become a teacher in Texas, you do not need a degree in education. If you are looking for a new career path, 240 Certification offers a teacher alternative certification program to help you become a certified teacher in Texas. Hear from these individuals who made the leap!
Absolutely! A huge perk of seeking alternative certification in Texas through a TEA-approved EPP is the ability to teach in a classroom while you earn your certification. 240 Certification has partnered with many Texas school districts to allow candidates to be hired and receive full pay and benefits while completing their year-long internship. Once you have completed 150 coursework hours, 50 observation hours, and passed your content exam(s), you will be issued a Statement of Eligibility (SOE). Once you have received your SOE, you can apply for your intern certification and begin teaching in your own classroom while earning your certification.
Texas does offer emergency teacher certification, but it’s managed by school districts—not certification programs. With several pathways available, the options can be confusing. Alternative certification remains one of the most streamlined ways to enter the classroom quickly. If you’re looking for a clear and supported path, choosing a program like 240 Certification can guide you through the process and get you teaching fast.
When starting a new career, you must consider what you will be paid for in those first few years. According to the NEA, the average salary for a starting teacher in Texas is $48,526. Once you have some earned years of service, veteran teachers earn an average of $62,463 in Texas.
Your costs will vary depending on the education preparation program you choose and what subject(s) and grade level certifications you seek. If you go the traditional route the cost will mostly be included in your college tuition. If you got the alternative route you can expect to spend around $5000-$7000 for the program cost, exam fees, and other certification costs.


